
Translated by AI
Electrical heart ablation using PFA technology: A new option for treating arrhythmia AF.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a condition that can increase the risk of stroke and heart failure. Treatment using Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) technology is a new option that helps in targeted therapy by using high-voltage electricity to ablate the heart tissue that causes the problem, without affecting the surrounding tissues. It offers quick recovery, reduces complications, and provides satisfactory clinical outcomes.

Translated by AI
How slow does the heart rate need to be before seeing a doctor?
The heart beating slower than usual can happen. It is important to monitor yourself, not ignore any abnormal symptoms occurring in the body, and promptly see a cardiologist for examination and treatment.

IRREGULAR HEARTBEATS OR CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA
The most common irregular heartbeats is caused by a conditon known as atrial filbrillation. This is when the heart’s upper chambers (the atria) beat chaotically. Patients with this condition are 10 – 15% at risk of stroke annually, as the irregular heartbeats can cause blood clots to form in the heart.

Women should not overlook cardiovascular disease.
Current researches have indicated that the most common health-related problems in women do not only include cervical cancer and breast cancer, but cardiovascular disease.

What Causes Irregular Heartbeat?
Irregular heartbeat or arrhythmias can be experienced by people of all ages. Common triggers can be but not limited to cardiovascular disease, thyroid disease, lifestyle, environmental, and genetic factors. Certain types of arrhythmia occur in people with severe heart conditions, and can cause sudden cardiac death. Some of these deaths could be avoided if the arrhythmias were diagnosed earlier.

LOVE your heart: “Love your heart...get informed for prevention and treatment” (Atrial Fibrillation)
Atrial Fibrillation (AF or A-Fib) is a condition that causes irregular heartbeats and can be found in 1-2% of the general population.

Translated by AI
Misconceptions about Arrhythmia
Misconceptions about Arrhythmia

Translated by AI
Arrhythmia is treatable
Arrhythmia is a condition where the heart beats too fast or too slow compared to normal. It may result from abnormalities in the generation of electrical impulses in the heart, the conduction of electrical impulses in the heart, or both.
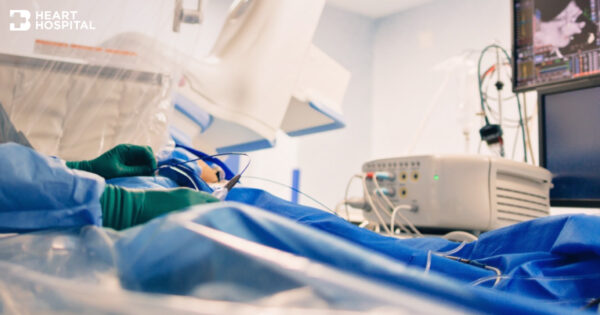
Translated by AI
Surgery to correct abnormal heart rhythm caused by Atrial Fibrillation
Surgery for correcting electrical short circuits in the heart. Surgeons at the Bangkok Heart Hospital perform surgery to correct electrical short circuits in the heart using minimal incision techniques or tools similar to surgical robots. This results in a 90% success rate. Patients can recover quickly from the surgery and can return to work within 1 – 2 weeks.
