CYP2C19 Pharmacogenomic Testing
Why Genotyping Changes Outcomes
Understanding the genetic factors in Clopidogrel activation.
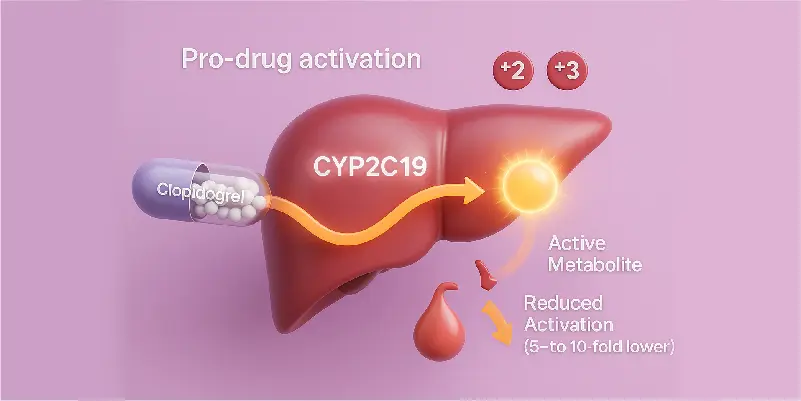
Pro-drug Activation
Clopidogrel requires activation by the CYP2C19 enzyme. Loss-of-function alleles can reduce active metabolite exposure 5 to 10-fold.
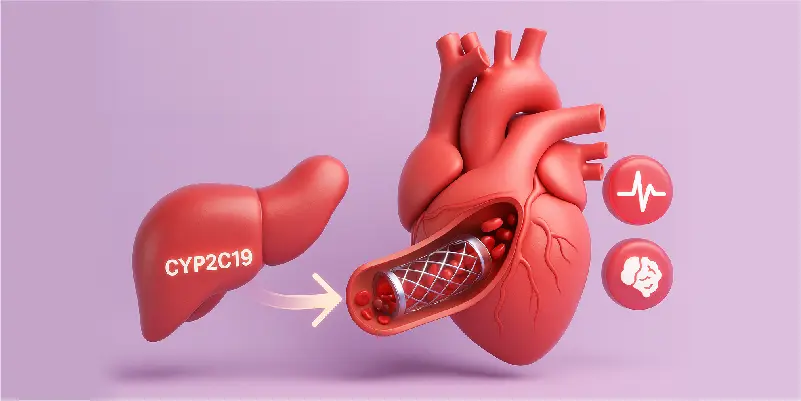
Clinical Risk
Intermediate & Poor Metabolizers (IM/PM) have significantly higher rates of stent thrombosis and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
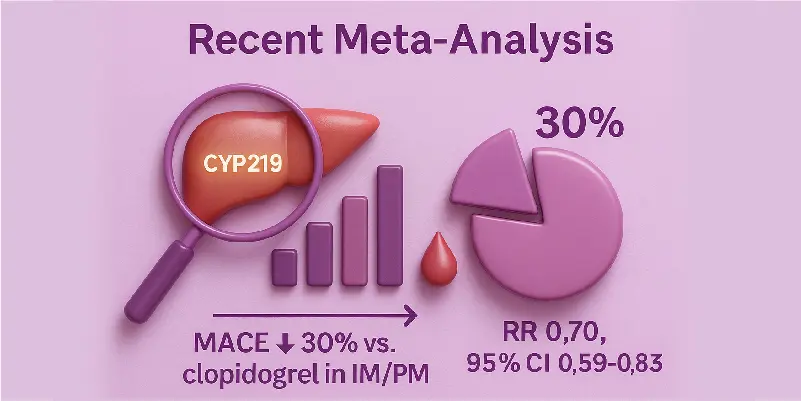
Recent Meta-analysis
Genotype-guided therapy lowered MACE by 30% in IM/PM patients compared to standard clopidogrel treatment.
| Group | How common are slow genes? | What that means for clopidogrel |
|---|---|---|
| East & South-East Asians | ≈ 1/2 people | Standard dose often too weak |
| Europeans | ≈ 1/4 people | Many do well, some need adjustment |
| Africans / African-Americans | ≈ 1/5 people | Mixed response; test to be sure |
| Hispanic / Latino | ≈ 1/ 5 people | Similar to African ancestry |
Who Should Be Tested?
Identifying ideal candidates for pharmacogenomic testing.
Your Journey with Genolife Services
A streamlined process for personalized antiplatelet therapy.
 |
Pre-test CounsellingDiscuss benefits, limits, inheritance, and alternative antiplatelet options. |
 |
Sample CollectionConveniently provide a 3 mL EDTA blood sample or use a saliva kit. |
 |
Expert InterpretationReviewed by a team including a Clinical Geneticist, Pharmacologist & Interventional Cardiologist. |
 |
Post testOffered for relatives with CAD who may also need antiplatelet therapy. |
Ready to plan for a safer health future?
Contact us for a consultation with our Genetic Counselor/Pharmacogenomics Specialist about the Clopidogrel Response Panel or other genetic tests.
Book a Consultation
References
- Hershfield MS et al. CPIC Guideline for HLA-B Genotype and Allopurinol Dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013.
- Saito Y et al. CPIC guideline update review, 2015.
- NCBI GeneReviews®. Allopurinol Therapy and HLA-B*58:01 Genotype. 2020 update.
- ACR Gout Management Guideline. 2020.
- Somkrua R et al. Meta-analysis: OR ≈ 74 for SJS/TEN in HLA-B*58:01 carriers. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011.
- Puangpetch A et al. HLA-B allele diversity in Thais: 16 % HLA-B*58:01. Hum Immunol. 2015.
- Tassaneeyakul W et al. Allopurinol-induced SJS/TEN and HLA-B*58:01 in Thai patients: sensitivity 100 %, specificity 87 %. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009.







