Life-threatening cerebral vascular disorders, especially diseases arising from congenital abnormalities of cerebral blood vessels like arteriovenous malformation (AVM) often show no symptoms until they become severe. Therefore, observing and understanding the disease should not be neglected.
What is AVM?
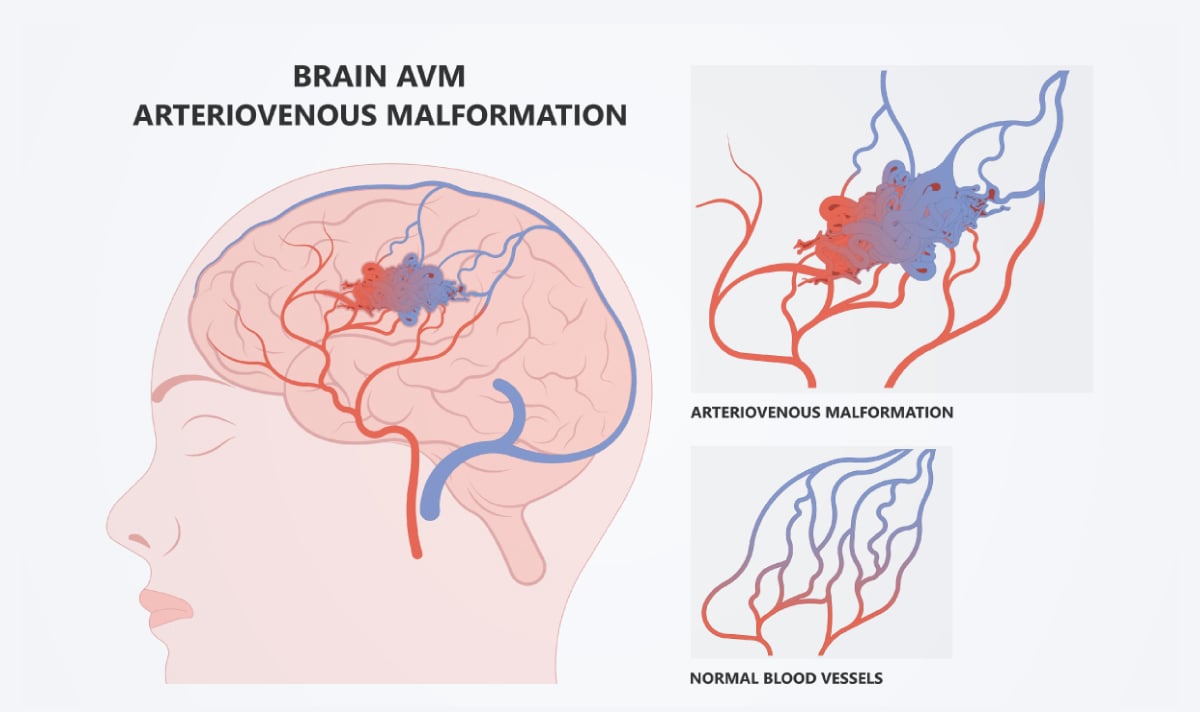
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) (AVM – Arteriovenous Malformation) or AVM is a condition often present from birth, caused by abnormal connections between arteries and veins, affecting blood and oxygen circulation in the affected brain area, leading to brain damage AVM can occur in various locations, is more common in males than females, primarily found in ages 20 – 30 years old, and in those with a family history of the condition.
What are the symptoms of AVM?
AVM symptoms can vary from one patient to another, depending on the size, location of AVM, and whether there is also an enlargement of the arteries. Symptoms that lead to a doctor’s visit can range from accidental discoveries through radiographic images, headaches, seizures, or symptoms of AVM rupture such as
- Bleeding in the brain tissue results in headaches, weakness in arms and legs, vomiting, and can be fatal.
- Bleeding in the brain surface or outer brain tissue results in seizures and abnormal brain electrical activity.
- Bleeding under the brain’s arachnoid layer (Subarachnoid hemorrhage: SAH) results in difficulty speaking, severe dizziness, limb numbness, vision loss, etc.
What triggers AVM?
- Genetics – If a family member has this condition, there is a chance of developing it.
- Increasing blood pressure – Blood vessels may rupture.
- Exerting too much force for a long duration – May result in vessel rupture.
- Decreased blood circulation – The brain may suffer from lack of blood, leading to seizures.
When to see a doctor
Since AVM (AVM) often shows no symptoms, if you experience headache, dizziness, blurred vision for more than 3 consecutive days without improvement after taking medication, it’s advisable to see a doctor for a detailed check-up.
How is AVM diagnosed?
Neurologists will diagnose AVM (AVM) using appropriate methods for each individual and evaluate using the Spetzler – Martin Grading Scale, including:
- Detailed history taking, especially regarding neurological abnormalities
- CT Scan to examine the details of the abnormal brain area clearly
- MRI to check for brain tissue changes and possibly locate the AVM
- EEG to examine brain cell function from the electrical activity displayed on the screen, diagnosing and assessing brain vascular diseases, epilepsy, etc.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) to inspect the shape, speed, and distance of blood circulation through vessels
- Bi-plane DSA or Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography to check brain vessels, standard for assessing the size of the lesion, evaluating rupture risks to aid in treatment consideration, and also as a treatment method for AVM.
How is AVM treated?
Treatment for AVM (AVM) aims to prevent bleeding in the brain and complications. For patients with large lesions, multiple treatment methods may be needed, depending on the symptoms, medical examination results, and doctor’s advice. The main treatment methods include
- Embolization involves blocking arteries to treat AVM by inserting a small tube to the problem site, then using small coils, glue, or balloons, as deemed appropriate by the doctor, to obstruct the vessel and reduce blood flow.
- Surgery to remove the abnormal vessels. Suitable for AVMs that are not too deep, with low risk. Risks increase with depth.
- Radiotherapy targets the abnormal blood vessels to gradually shrink the lesion
Can AVM recur?
Once treated, AVM (AVM) can recur, although the chances are low. Possible reasons include incomplete treatment, such as not all vessels shrinking or the lesion being too large. Therefore, choosing treatment with a specialized and experienced doctor and team, and a modern-equipped hospital is crucial.
Can AVM be prevented?
AVM (AVM) cannot be prevented as it is often congenital. However, recurrence after treatment can be prevented by avoiding sudden high blood pressure, not exerting excessively, avoiding heavy lifting, controlling seizures as per doctor’s advice, ensuring sufficient rest, avoiding alcohol and cigarettes, and managing stress effectively.
Experts in treating AVM (AVM)
Dr. Titima Itthimathin is a specialist in neurosurgery at the Hospital for Bone and Brain.
Hospitals specializing in AVM treatment (AVM)
The Brain and Nervous System Center at the Hospital for Bone and Brain is ready to treat arteriovenous malformation (AVM) with a team of specialists experienced and modern technology to restore quality of life.












