What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a malignant change in cells on the skin and mucous membranes. There are many types of skin cancer, with the most common being basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
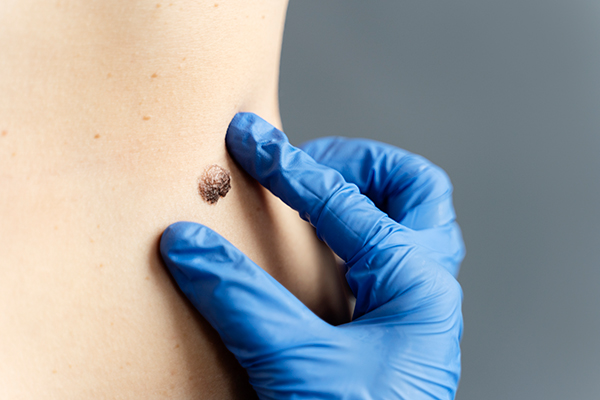
Skin cancer is a malignant change in cells on the skin and mucous membranes. There are many types of skin cancer, with the most common being basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
The exact cause of skin cancer is currently unknown, but risk factors have been identified as follows:
Skin cancer occurs on the skin, visible to the naked eye, and can occur throughout the body. Symptoms of skin cancer vary depending on the type of skin cancer, as follows:
It can be of many colors, from black, red, pink, brown, and gray. The color of the skin cancer is not uniformly distributed on the lump. It is the least common type, but it is highly aggressive because it is more likely to spread to nearby tissues and other areas than other types, and can quickly enter the bloodstream. If left untreated, it can cause death within 3-6 months.
Stage 1: The lesion is no larger than 2 centimeters (the 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 90-100%).
Stage 2: The lesion is larger than 2 centimeters or any size, but the cancer cells are highly proliferative or have spread deep beneath the skin (the 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 70-80%).
Stage 3: The disease has spread to other tissues adjacent to the skin, or to a single nearby lymph node, and the node is no larger than 3 centimeters (the 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 50%).
Stage 4: The lesion has spread to the bone or nerves, to more than one lymph node, or to a lymph node larger than 3 centimeters, or to the bloodstream. When spreading, it often extends to the lungs. (The 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 0-30%)
Stage 1: The lesion is 0-1 millimeters deep. (The 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 75-80%).
Stage 2: The lesion is 1 millimeter or more deep. (The 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 40-70%).
Stage 3: The disease has spread to the lymph nodes. (The 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 30-40%).
Stage 4: The disease has spread to the bloodstream, often to the lungs, bones, and brain. (The 5-year survival rate after treatment is approximately 0-10%).
There are several preliminary screening methods, including:
Early Skin Cancer Assessment: Since skin cancer treatment is most effective and curable when detected early, those with the aforementioned risk factors should periodically examine their entire body. This can be done using a standing mirror or a hand mirror. The examination steps are as follows:
A: Asymmetry: The asymmetry of the skin lesion on each side.
B: Border irregular: The edges of the skin lesion are irregular and unclear.
C: Color multiple: The color of the lesion is uneven and changes color.
D: Diameter > 6 mm. or Ugly duckling: The structure of the skin lesion is larger than 6 mm.
E: Evolution in the last 3 months: There has been a change in size and shape over the past 3 months.
For cases of extensive or inoperable tumors, or cancer that has spread to other areas, or melanoma that has already metastasized, doctors may prescribe radiation therapy in combination with chemotherapy. Treatment results are generally successful and can lead to a complete cure.
Those at high risk, such as those with a family history of skin cancer or those who work in the sun, should see a doctor for early skin cancer screening at least once a year.