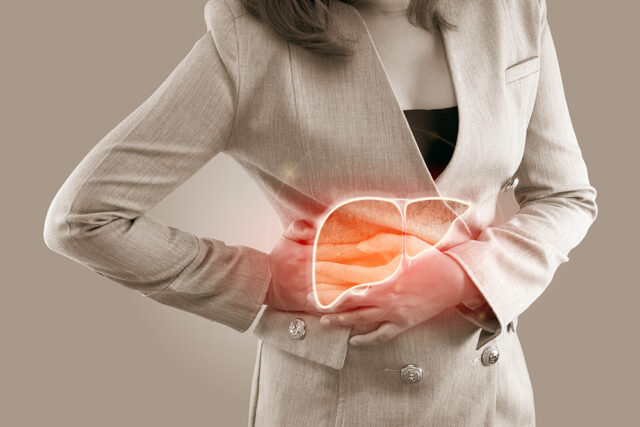
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is the most common cancer in Thai men. It typically occurs in people aged 30-70 years. It is 2-3 times more common in men than in women, as men have higher risk factors than women. Early-stage liver cancer often has no symptoms. There are two types of liver cancer:
Primary liver cancer arises directly from liver tissue and is divided into two categories: hepatocellular carcinoma and bile duct carcinoma.
Secondary liver cancer is caused by metastasis from other cancers, such as lung cancer and breast cancer.
Factors and Risks of Liver Cancer
The most common risk factor for liver cancer is hepatitis B infection, which is primarily transmitted from mother to child. However, in developed countries, the primary cause of liver cancer is alcohol consumption.
Liver Cancer Diagnosis and Screening Methods
Liver cancer diagnosis includes:
- History taking and physical examination
- Blood test for the liver cancer marker “alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)”
- Implantation imaging (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI)
- Biopsy
Liver cancer screening is recommended for those at risk:
- Patients with cirrhosis of any cause
- Patients infected with hepatitis B or C, or carriers of these viruses
- Men over 40 and women over 50, or with a family history of liver cancer due to hepatitis B infection, should see a doctor for an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test and a liver ultrasound every 3-6 months.