What is cervical cancer?
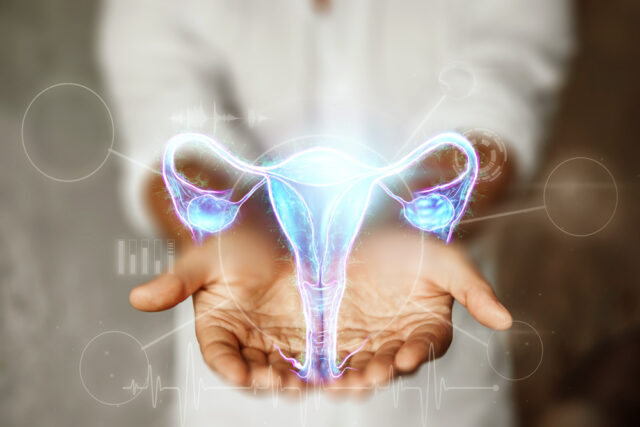
The cervix is the part of the female reproductive organ that extends from the uterus in the abdominal cavity into the vagina. It is the passageway for menstrual blood, which flows from the uterus and out through the vagina during intercourse. Semen travels into the vagina and enters the uterus through the cervix. When fertilization occurs with a woman’s egg, a baby is born, residing in the uterine cavity and being born through the vagina at term.
Cervical cancer is a cancer of the female reproductive organs. It is the most common cancer in Thai women and causes numerous deaths from this disease.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
The main cause of this disease is the human papillomavirus (HPV), also known as HPV, which is transmitted from person to person through sexual contact. A woman may have been infected with this virus in her lifetime, but her body can eliminate it. However, some women cannot eliminate the virus. There are also other risk factors that cause changes in cervical tissue and lead to diseases such as genital warts, cervical cancer, and others.
How many stages are there of cervical cancer?
The doctor will need to perform additional tests to determine the stage of cervical cancer. There are four stages of cervical cancer:
Stage 1 is the early stage.
Stages 2 and 3 are intermediate.
Stage 4 is the final stage. The cancer may have spread to other organs in the body, such as the liver, lungs, or bones.
Cervical Cancer Screening
Cervical cancer screening refers to the detection of changes in cervical tissue cells before symptoms appear. This screening detects precancerous lesions and early cancers, enabling effective treatment and prevention of cervical cancer, including early cancer treatment.
- Cervical cytology, or Pap smear, is performed by a doctor during a pelvic exam. After the exam, the doctor will schedule an appointment to hear the results or inform you of the results. If any abnormalities are found, treatment will be initiated based on the lesion.
- Cervical cancer screening using cytology combined with testing for high-risk HPV types. This screening method has the advantage of allowing doctors to provide better care for abnormal cervical cells. However, it has the disadvantage of significantly increasing patient costs. Currently, Thai women are recommended to have a pelvic exam and a Pap smear if they have been sexually active for approximately three years, are over 30 years old, or have other risk factors.
- Bangkok Rayong Hospital Cervical cancer screening services are available by combining HPV DNA testing with a Pap smear (or Pap Test) to look for cell abnormalities at the same time, also known as Co-testing. The HPV DNA test tests for HPV, which is the main cause of cervical cancer, up to 90%, while the Pap smear tests for cell abnormalities that could turn into cancer in the future. Therefore, testing both methods together will give doctors a higher chance of detecting cancer in the early stages than testing with a Pap smear alone.