Tonsillitis commonly occurs in both children and adults alike, but the level of the symptoms may vary. If a person suffers from the condition persistently – i.e., many times within a year – it can become chronic and severe. So, if any symptom is detected, you should not be too complacent but, rather, consult a doctor and have the condition treated so that you can enjoy life to the fullest every day.
The Tonsil Glands
Tonsils are a pair of soft tissue glands containing different types of white blood cells. They are located at the back of the throat on each side, and are a part of the lymphatic system that helps prevent viruses from entering the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. One of their functions is to produce antibodies when the body is fighting infection. A common ailment associated with the tonsils is tonsillitis or unexpectedly enlarged tonsils. This condition can interfere with the patient’s breathing as well as swallowing ability.
Acute Tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis is a common cause of sore throats among both adults and children. It is more frequently found in children younger than 10 years old. Generally, the cause of the inflammation stems from infection by bacteria or virus. Some of the symptoms include sore throat, sharp inner-ear pain, fever and chills, painful or difficulty swallowing, swollen glands around the neck area, drooling or vomiting after a meal in children. If the inflammation occurs often – repeatedly many times a year – the tonsils can become enlarged as the condition turns chronic. This could also be the cause of bad breath.
Acute Tonsillitis Treatment
For acute tonsillitis, normally the doctor will consider treating the symptoms: for examples, painkillers, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drug based on the particular type of suspected bacteria. If antibiotic is prescribed, it is necessary for the patient to continue the medication for at least 7 – 10 days. And if the symptoms do not improve but remain severe with high fever in addition dehydration as well as malnutrition, hospitalization may be required for intravenous medication. In cases where other complications arise – e.g., expanded area of inflammation, abscess is formed around the tonsils, or the infection has entered into the bloodstream which can be a life-threatening condition – surgery may be needed together with other remedies to drain the abscess.
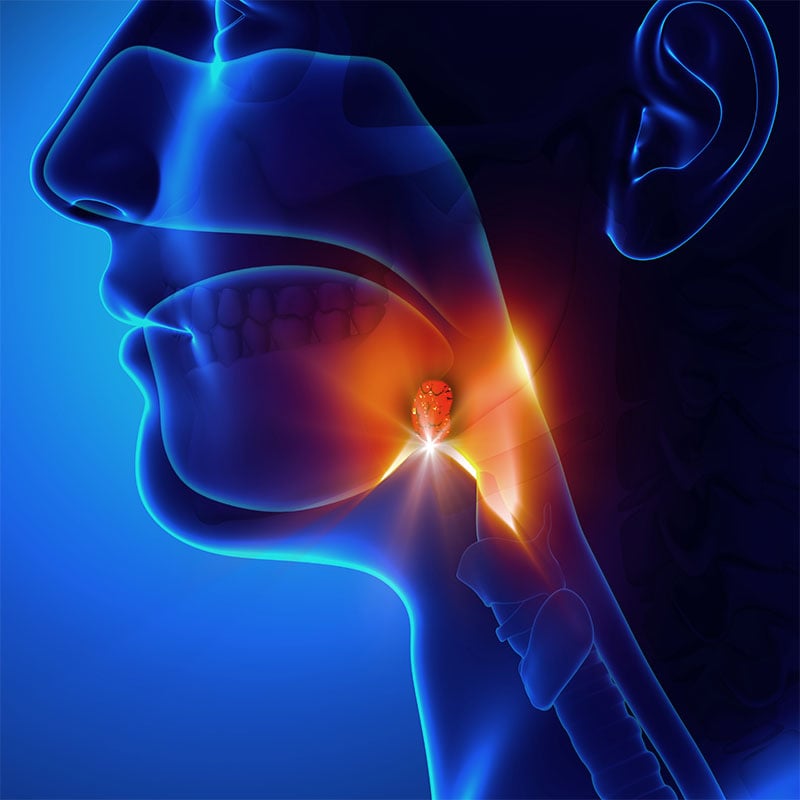
Tonsillectomy Surgery
For a chronic tonsillitis case, when the tonsils are frequently inflamed or they have become so enlarged that they interfere with the breathing or the ability to swallow food, tonsillectomy surgery may be considered to relief the symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. The surgery will require general anesthetic, after which the doctor will use electrocautery or a special tool (such as a sharp scalpel) to remove the tonsils through the patient’s mouth. For about 1 week after the procedure, the patient may feel some discomfort in the throat or has some difficulty swallowing food, but the condition will improve and return to normal after 2 – 4 weeks.
When Should Tonsillectomy Be Considered?
- The patient suffers from chronic tonsillitis, persistent sore throat, or has been treated for abscess around the tonsils with antibiotic but the condition has not improved, or the tonsils have become a source of chronic bacterial infection.
- Repeated inflammation, such that it interferes with the patient’s quality of life – e.g., fever, sore throat, feeling sick and have to miss work or school often.
- There is a complication as a result of the inflammation – e.g., abscess around the tonsils or in the throat. In this case, it is recommended the tonsils be removed to prevent more severe problems in the future.
- The tonsils have become enlarged and are impeding the air passageway, making it difficult to breath, or are causing snoring or sleep apnea.
- There is a potential for tonsil cancer or other types of tumor in the tonsils
Care After Tonsillectomy
During the week after the surgery, the patient should follow the guidelines below:
- Eat soft food that is not too flavorful.
- Avoid rough food that may hurt the wounds in the throat.
- Avoid forceful coughs or expectorating of phlegm.
- Avoid strenuous exercises that could cause the wounds to split.
- If there is excessive bleeding from the wounds, consult the surgeon immediately.
Misconception About Tonsillectomy
There is a misconception that tonsillectomy reduces the patient’s immunity because there is no longer a gland to capture germs, making the patient susceptible to infections. This is not true. It is because tonsillectomy is recommended only by a doctor after it has been determined that the tonsils are not functioning properly and, instead, they may become the source of infections. In addition, the human body possesses other sufficient lymphatic resources and the surgery does not have effect on the immune system in any way.
Many patients are concerned about soreness in the throat or difficulty swallowing after tonsillectomy. However, surgeons nowadays have many special options at their disposal: such as utilizing high-frequency radio waves for the surgery and stopping the bleeding at a low temperature. This technique causes less trauma to the tissue and allows for faster recovery than the traditional method. In any case, if you are suffering from tonsillitis, it is recommended that you consult a specialist and receive a treatment as soon as possible.