Enhance diagnosis accuracy. Promote treatment safety.”
Get to know “rheumatic diseases and genetic testing”
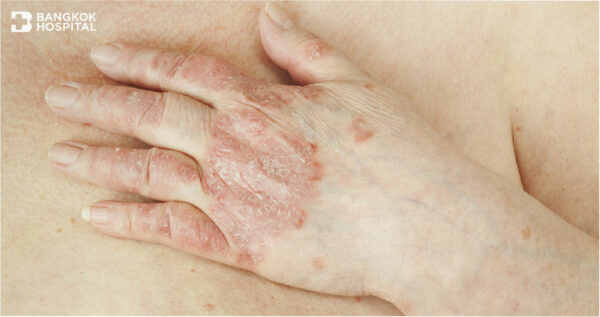
Rheumatic diseases refer to a group of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders affecting joints, cartilages, tendons, ligaments, muscles and bones. Evidence favoring genetic predisposition to different rheumatic diseases has been revealed, such as the HLA-B27 test aiding in confirmatory diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis and the HLA-B5801 test evaluating the risk of severe adverse reactions to allopurinol – uric acid lowering agent used in gout treatment. In addition, other genetic tests are aimed at detecting or ruling out the presence of hereditary predisposition to rare conditions causing inflammations and affecting a wide range of body parts.
Find out the role of HLA-B27 gene in ankylosing spondylitis
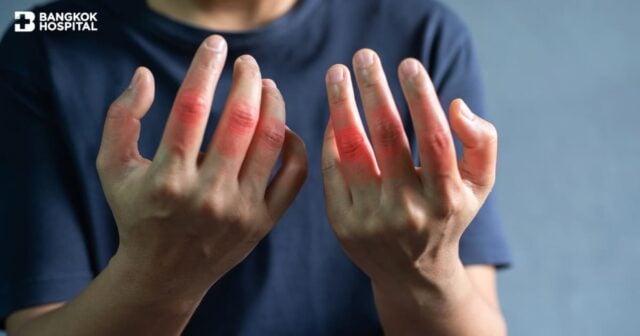
Ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis that causes chronic back pain, is often found in children, adolescents and young adults. With or without joint inflammation, symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis might include back pain and stiffness in the back, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. To diagnose ankylosing spondylitis, it usually involves the examination of signs and symptoms, blood tests to check for markers of inflammation, and x-ray of sacroiliac joints and MRI scan. Interestingly, people who have a HLA-B27 gene are at a greatly increased risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis. Therefore, genetic test for the HLA-B27 gene helps aiding diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis while taking into account other relevant tests.
Find out the role of HLA-B5801 gene in gout treatment
Regarding treatment aspect, the role of genetic testing to enhance safety has been addressed in patients diagnosed with gout brought on by the accumulation of uric acid in the joints, causing the inflammation and intense pain. The treatment goal is to lower the amount of uric acid in your blood while reducing the inflammation and pain associated with gout attacks. If left uncontrolled, too high level of uric acid in the blood repeatedly induces inflammation of the joints, urging the patients to take excess amount of pain killers and putting the patients at greater risk of experiencing undesired effects, such as kidney failure. Several medications used to lower the level of uric acid are available. Among these medications, allopurinol is widely prescribed. Although it is generally well tolerated, allopurinol is associated with life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions in some patients. The HLA-B5801 gene has been proven to be a genetic marker for allopurinol-induced severe hypersensitivity. If the HLA-B5801 allele is present, allopurinol is no longer first-line treatment and other medications must be prescribed instead.
What are benefits of genetic testing in rheumatic diseases?
Genetic testing plays significant roles in rheumatic diseases, including: assisting diagnosis of certain diseases, e.g. ankylosing spondylitis and Behçet’s disease, promoting treatment safety, e.g. gout treatment using allopurinol and detecting or ruling out the presence of hereditary predisposition to rare conditions related to rheumatic or autoinflammatory conditions. Whether genetic testing is recommended in each individual, the consideration is made by the expert rheumatologist grounded on indication and manifestations along with other relevant laboratory tests.
Precision Medicine more accurate diagnosis for rheumatic diseases”