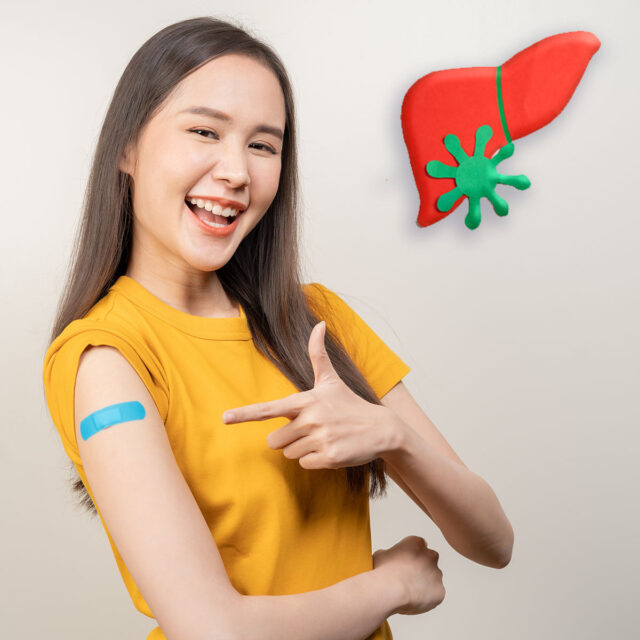
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) is one of the solutions for vision problems suitable for people over the age of 50 who experience lens changes. The lens begins to deteriorate, changes color, and becomes cloudy with cataract formation, allowing them to see clearly at any distance and reduce the usage of glasses.
What is Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)?
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) is an eye surgery procedure that involves removing the natural lens, similar to cataract surgery, and replacing it with an Intraocular Lens (IOL) that has been calculated based on the patient’s vision measurements. This helps adjust the refractive power and reduces the need for glasses or contact lenses, addressing vision problems. For those without significant cataracts, small incision cataract surgery can enhance clarity of vision.
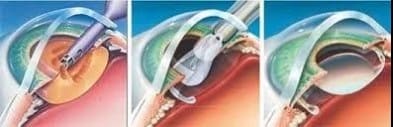
Who is Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) suitable for?
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) is suitable for correcting vision abnormalities in individuals aged 50 – 55 years and older who wish to improve their eyesight while reducing dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This procedure is similar in purpose to those in the younger age group 20 – 50 who aim to reduce the use of glasses or contacts through LASIK or additional lenses. However, due to age-related limitations, laser or additional lens treatments might not be suitable.
Typically, individuals aged 20 – 50 correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and presbyopia using laser vision correction like Femtolasik, Femtolasik presbyond, PRK, ReLEx SMILE, depending on the suitability of their vision parameters. Those aged 20 – 45 with high myopia or thin corneas unsuitable for laser treatment and still having clear lenses may opt for additional lenses ICL.
For individuals aged 50 – 55 and older with abnormal vision such as myopia, hyperopia (both congenital and age-related), and astigmatism, who dislike wearing glasses or contacts, treatments like Femtolasik, ReLEx SMILE or additional lenses ICL might have limitations. As the lens changes more with age, Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) is becoming a suitable solution for correcting vision problems in this age group.

Types of Lenses Used in Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)

1) Monofocal IOL Single Vision Lens (1 Distance Focus)
This type of lens provides clear vision at a single distance, typically calculated for clear far distance focus.
1.1 High Correction Monofocal Lens for Clear Far Vision in Both Eyes (Full Correction)
Treatment Results: Post-surgery, the refractive power can be corrected.
- Clear far vision without glasses.
- Requires reading glasses for clear near vision. Less chance of disturbances in dark environments such as halos or glare compared to other lenses.
1.2 Single Vision Lens with Different Focus in Each Eye (Monovision)
- Dominant eye: lens focused on clear far distance
- Non-dominant eye: lens chosen to focus on near distance
Treatment Results: Post-surgery, the dependency on glasses is reduced.
- When using both eyes simultaneously, can see both near and far for those who can adapt (similar to Monovision Lasik).
- The doctor will need to test beforehand to ensure that the patient can adapt and see well at close and far distances, and evaluate suitability based on previous use of glasses or contact lenses.

2) Multifocal IOL / Trifocal IOL Multiple/Varying Distance Focus Lenses
These lenses are designed to provide clear vision at multiple distances, featuring multiple concentric rings reducing the need for glasses. They include several focal points for far, intermediate, and near vision, enabling each eye to see at various distances. Approximately 80 – 90% of users can perform everyday tasks like reading, using computers, and driving without glasses, but for very small print or low light tasks, glass assistance might still be needed.
Trifocal IOL lenses offer superior near vision compared to single vision or EDoF lenses, but might come with increased light disturbances in dark environments. Most users adapt over time, though the speed varies per individual.

3) Extended Depth of Focus IOL (EDoF IOL) Lenses Extending or Stretching Focus Range
EDoF lenses are designed for clarity from far to intermediate distances, with some near vision capability, causing fewer light disturbances in the dark compared to multifocal lenses. EDoF IOL technology varies, with newer models not featuring multiple concentric rings but instead using lens curvature technology for extended vision range, minimizing daily glasses use and enhancing convenience. They provide continuous vision with clarity over a broader range, especially at far and intermediate distances.
- Better for computer use or cooking than single vision lenses, with usable near vision, though not as crisp as trifocal lenses (Trifocal IOL), yet reducing glasses dependence more than single vision lenses.
- In low light or nighttime usage, EDoF IOL reduces issues like halos or glare often found with trifocal lenses.
Lenses reducing glasses dependency, such as multifocal or EDoF IOL, differ from bifocal or progressive glasses due to their design, which eases adaptation and vision. The brain learns to focus automatically, taking about 1 week to 1 month for improved close tasks like reading or mobile use and intermediate tasks like computer use or cooking. As time progresses 3 – 6 months, clarity and adaptation increase, with night light disturbances decreasing.
After selecting one of the three primary lens types that meet your needs, if any eye has astigmatism due to uneven corneal curvature (determined by assessment), the doctor will recommend Toric IOL lenses to correct astigmatism as an enhancement in the main lens types to provide the sharpest image, determined by corneal curvature / astigmatism values specific to each eye, not directly related to pre-surgery vision.
Limitations after Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
- Light disturbance in dark environments, commonly found with multifocal lenses. Frequent issues include halos, rings, glare, or starburst around lights at night, especially while driving. However, post-surgery light disturbances are usually less than short-sighted, astigmatism, or cataract-induced disturbances.
- Within 3 – 6 months post RLE, the brain adapts to decrease light disturbances, though they may not vanish entirely. Most patients adjust enough that these disturbances don’t affect daily life or nighttime driving, though a few may experience intolerable visual disturbances.
- Reading or tasks requiring detailed vision need adequate lighting. Driving in darkness may make roadside object visibility challenging, requiring caution and initial adaptation.

Complications from Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) uses the same method as cataract surgery, with similar risks and complications, most of which are manageable, including:
- Increased risk of retinal detachment in those with high myopia
- Eye infections
- Bleeding within or beneath the retina
- Lens misalignment
- High intraocular pressure leading to glaucoma over time
- Swelling of the macula after surgery
- Lens capsule sagging or tearing, potentially necessitating single vision lens
- Temporary corneal swelling post-surgery for 1 – 2 weeks, rarely permanent
- Temporary dry eyes for 3 – 6 months post-surgery
Post-operative Care for Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE)
- Eye usage back to normal in about 1 – 2 weeks post-surgery
- Rest the eyes for 3 – 5 days, avoiding strenuous work or dusty environments
- Use computers and read around 3 – 5 days post-surgery
- Avoid water contact for at least 2 weeks
- Be cautious of dust and smoke
- Wear glasses or UV sunglasses
- Use a protective eye shield when sleeping for about 2 weeks
- Avoid bending below waist, lifting heavy objects for 2 – 4 weeks
- Avoid rubbing or pressing the eye socket post-surgery for 1 month
- Avoid exercise for about 1 month, but walking and stairs are fine
- Strictly follow prescriptions of antibiotics for 2 weeks and anti-inflammatory medication for 1 month
How to Select the Suitable Power for Intraocular Lenses
New technology currently provides tools and formulas to calculate the lens power needed, based on preoperative measurements such as corneal curvature, eye length, and various intraocular parameters, ensuring the most appropriate post-operative vision. If post-surgical vision isn’t sharp enough, corrective glasses or laser adjustments may be needed, evaluated by ophthalmologists.
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) provides a long-term solution for vision adjustment, especially for those over 50, by replacing the natural lens with a customized intraocular lens suited to individual needs. It enhances vision clarity and reduces dependence on glasses or contacts in daily life. However, it’s not suitable for everyone. Thorough research, consideration of its advantages and limitations, and a detailed eye consultation with a skilled ophthalmologist are vital for satisfactory results.
Why Choose Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) at Bangkok Hospital?
- Experienced, trained ophthalmologists with expertise and extensive experience
- Detailed pre-operative evaluation using modern medical tools and a multidisciplinary team
- Availability of newly designed intraocular lenses tailored to specific individual needs
- Complete care from assessment, surgery to post-operative follow-up
Which Hospitals Specialize in Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) Surgery?
Bangkok Hospital Eye Center is ready to perform Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) that meets lifestyle needs with a specialized and experienced ophthalmology team and multidisciplinary support to offer close consultation and advanced cataract surgical tools for comprehensive eye health restoration.
Expert Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) Surgeons
Dr. Tarinee Sa-Ngiampornpanit, Expert Ophthalmologist in Corneal and Refractive Eye Surgery, Cataracts, Bangkok Hospital
You can click here to schedule an appointment yourself.
Eye Surgery Packages
Eye surgery packages at Bangkok Hospital Eye Center start from 75,000 THB
For details on eye surgery packages, click here












