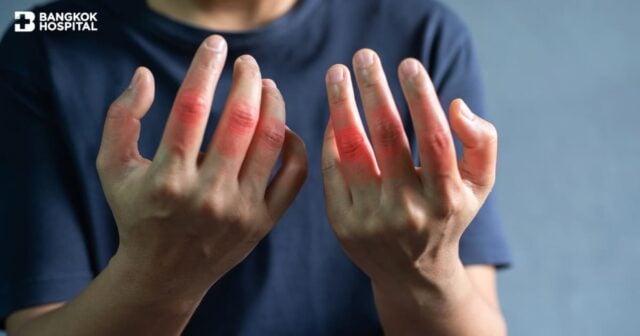
Many people often understand that “gout” is a common joint disease, just having swelling pain. However, in reality, gout is not just joint pain, but it may be the starting point of long-term health problems. If left uncontrolled for a long time, without managing uric acid levels well, it could lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease.
What is Gout?
Gout is an arthritis disease caused by high uric acid levels in the blood (Hyperuricemia) for an extended period until crystals accumulate in the joints, causing acute inflammation, severe swelling pain. It can be treated and prevented from recurring if following the doctor’s advice and appropriate care.
Common Risk Factors for Gout
- Genetics or family history of gout
- Men aged 30 – 50 years or postmenopausal women, during which hormonal changes affect uric acid excretion in the body
- Those who consume high-purine foods, such as animal organs, seafood, etc.
- Those with certain coexisting diseases such as chronic kidney disease, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia
- Those who take certain medications, especially diuretics (Diuretics) that increase uric acid levels in the blood and stimulate gout
- Those who frequently consume alcohol
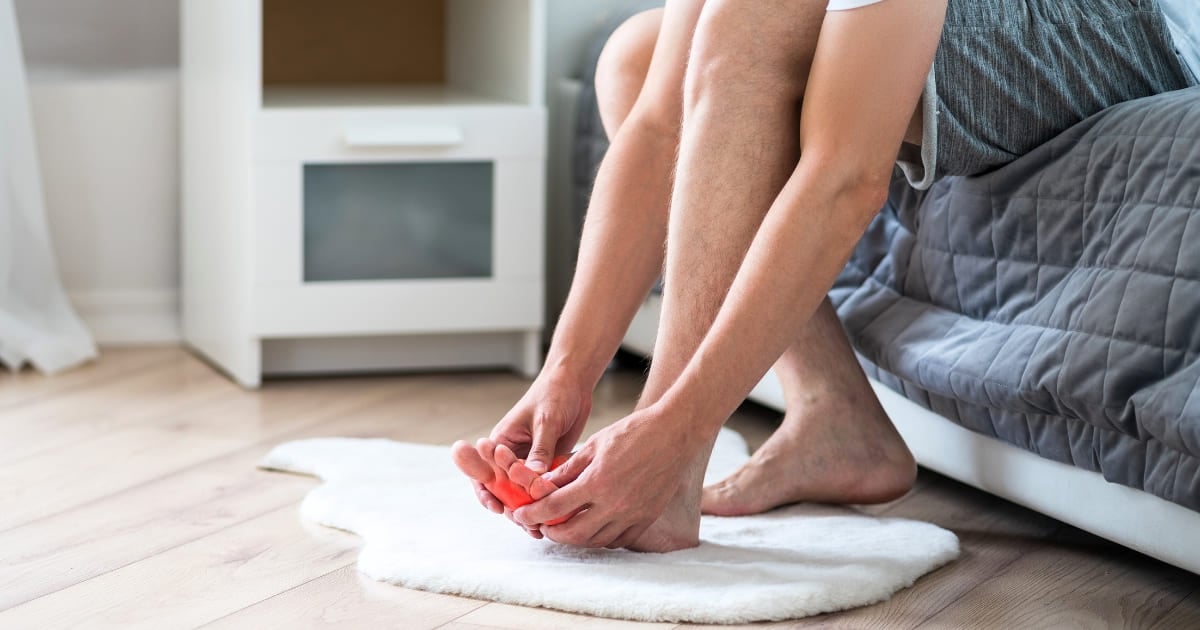

What are the Symptoms of Gout?
Gout often starts with acute joint pain, especially at night. The painful joints usually swell, turn red, feel hot, and are very tender. It usually starts in one joint, such as the base of the big toe or ankle. The pain may be so severe that it makes walking difficult and bearing weight impossible. Symptoms tend to come and go, but without continuous treatment, it may become chronic arthritis. Additionally, some may find “Tophi“, which are uric acid crystals collected under the skin.
How is Gout Diagnosed?
Gout diagnosis involves several components, such as
- Taking history and physical examination
- Blood test to measure uric acid levels (>6.8 mg/dL)
- Joint fluid aspiration to view uric acid crystals (Monosodium Urate Crystals) under a microscope
- X-ray, Ultrasound, or DECT of the joint in case of suspected gout crystal accumulation
Guidelines for Gout Treatment
- Acute Stage Treatment by physician using
- NSAIDs anti-inflammatory drugs
- Gout pain relievers Colchicine
- Steroid medication (in case of contraindications to other drug groups)
- Disease Control Stage Physician’s treatment using
- Uric acid lowering medications such as Allopurinol, Febuxostat
- Controlling co-morbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, blood lipids
- Regular blood test to monitor uric acid levels
- Self-Care (Self-Care)
- Gout patients should avoid high-purine foods like animal organs, seafood, and fructose sugar, which can increase uric acid levels in the blood.
- Avoid alcohol, especially beer, as it affects uric acid excretion in the body.
- Drink enough water, at least 2 liters per day, to reduce uric acid accumulation.
- Maintain a normal weight range
- Exercise regularly
- Strictly take medications as prescribed by the doctor
- Regular blood tests to monitor uric acid levels and prevent long-term complications
Where to Find a Hospital Specialized in Gout Treatment
Bangkok Hospital’s Rheumatology Clinic is ready to provide evaluation, diagnosis, care, and advice to gout patients with a specialized team of doctors and a skilled multidisciplinary team to ensure a good quality of life for patients.
Specialized Physicians
Dr.Thipsukhon Sathapanasiri, a rheumatology physician at the Rheumatology Clinic, Bangkok Hospital
You can click here to make an appointment by yourself.