Cholecystectomy
General Information
Reason for surgery
- Gallstones can be found and cause no symptoms.
- Asymptomatic patients do not require treatment.
- In symptomatic patients, gallstones can cause
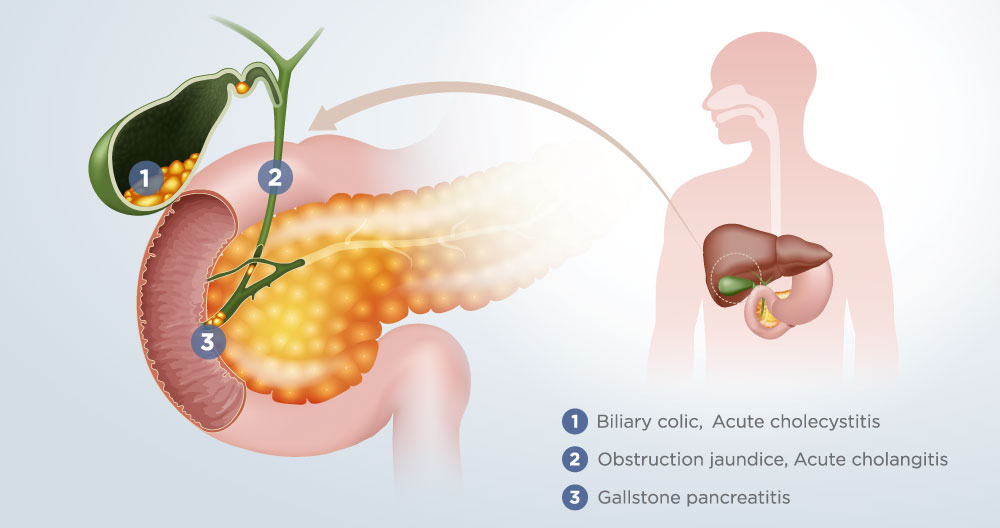
- Biliary colic
- Cholecystitis
- Cholangitis
- Pancreatitis
- Some symptoms of gallstones can be serious such as cholangitis, pancreatitis and treatment will be more complicated.
- In some patients, additional procedure such as ERCP may be needed.
- One third of the patients will experience recurrent symptoms if gallbladder still left inside their body.
- Cholecystectomy is the gold standard of gallstones disease treatment.
- Bile production and liver function are not affected by cholecystectomy.
- After surgery, patients can live as usual.
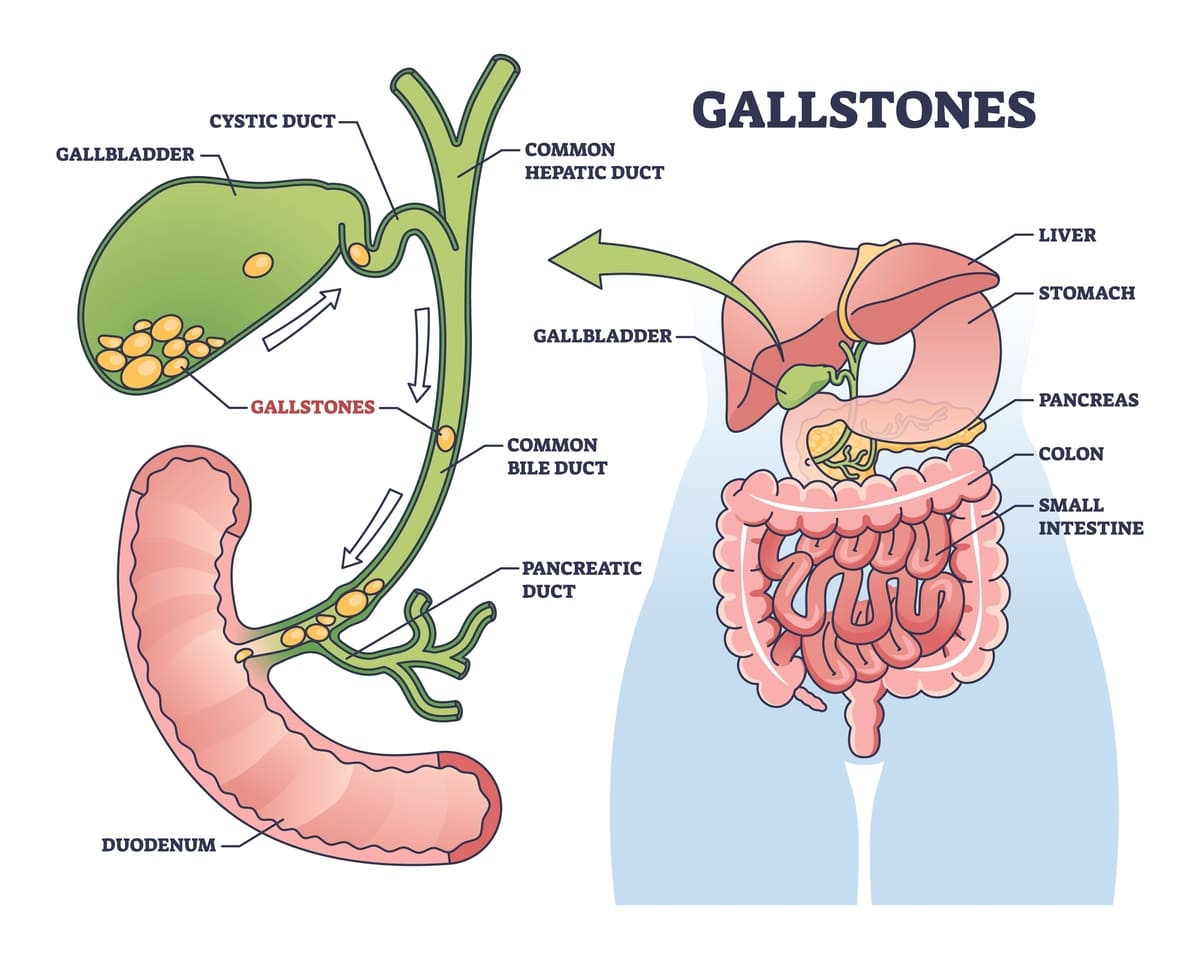
Anatomy of Gallbladder
- A pear-like organ located at right upper quadrant of abdominal cavity.
- Attach to the lower part of liver.
- Gallbladder itself does not produce bile.
- Bile production comes form the liver.
- Gallbladder will store and concentrate the bile.
- When you have a meal, gallbladder will contract to make the bile go into the bowel to help digested food especially fatty food.
Operative
About the Procedure
Cholecystectomy can be done in 2 ways
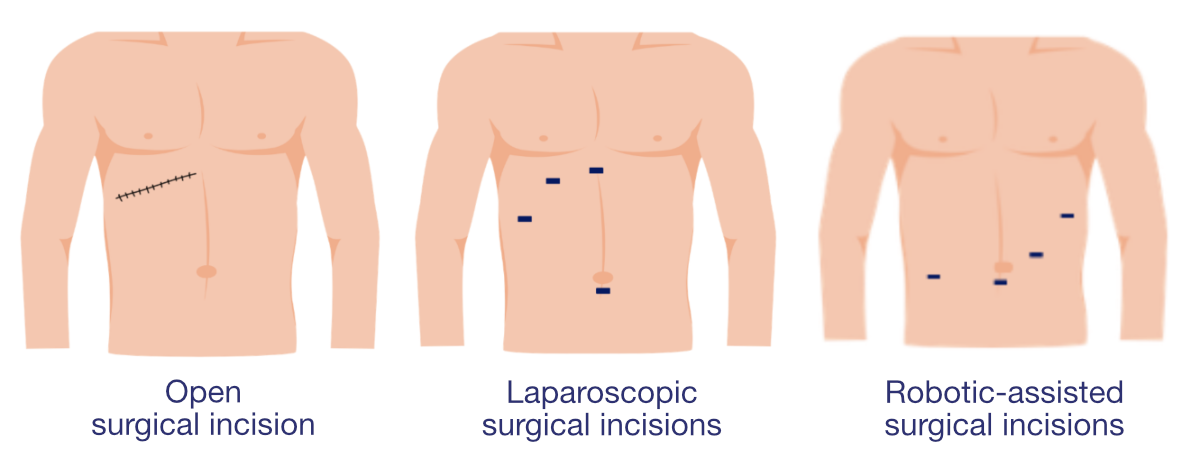
1. Minimally Invasive gallbladder Surgery
Minimally Invasive gallbladder Surgery is the standard treatment nowadays. Because of small incision, patient will have faster recovery and less pain.
- The procedure is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully asleep and comfortable.
- The surgeon makes 3–4 small incisions to insert a camera and instruments.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas is introduced to inflate the abdomen and create working space.
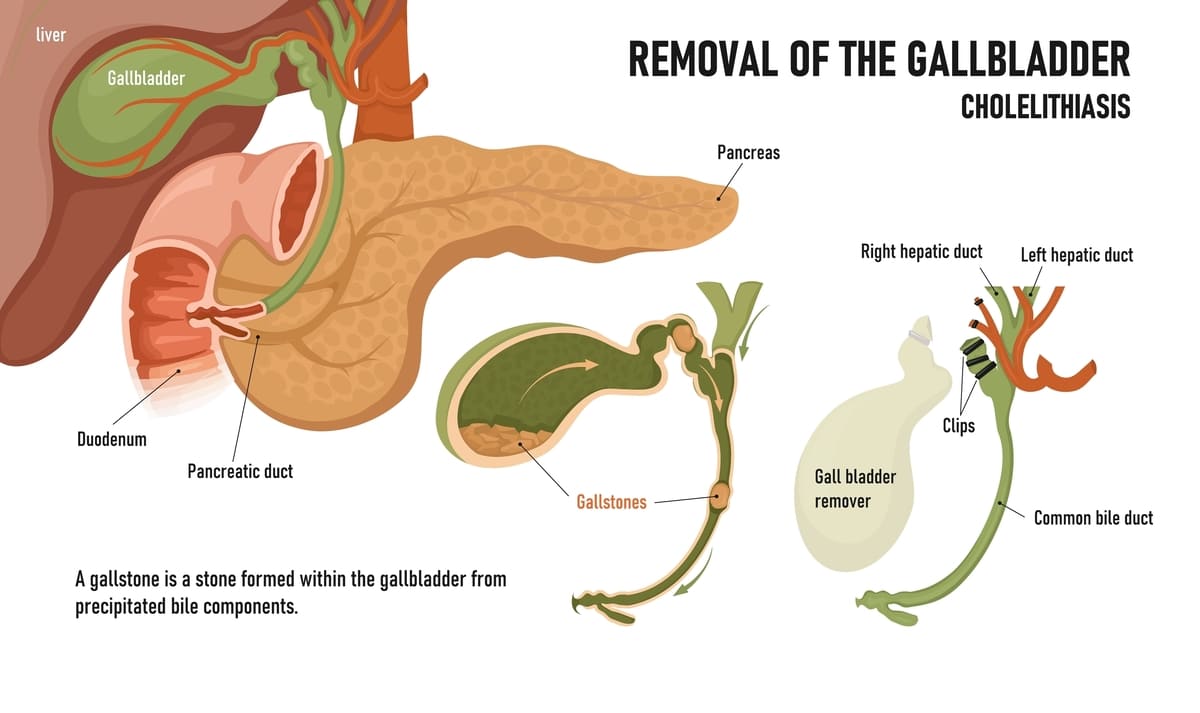
- The surgeon ligates the cystic duct using sutures or clips.
- The gallbladder is dissected and separated from the liver.
- The gallbladder is placed in a retrieval bag and removed through the belly-button incision.
- The gallbladder is opened after removal to collect the stones for the patient.
- The specimen is sent to pathology for detailed examination.
- All CO₂ gas is released at the end of the procedure.
- Small incisions allow faster recovery and less pain.
- Most patients stay in the hospital for 1–2 nights.
In some difficult situation, doctor may consider changing form small incision to open surgery, meaning change from Minimally Invasive gallbladder Surgery to open cholecystectomy
There are 2 types of minimally invasive gallbladder surgery:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This is the current standard treatment for gallbladder removal.
- Robotic-Assisted Cholecystectomy This is an advanced surgical technology in which the robot does **not** perform the surgery on its own.
Instead, it assists the surgeon by enhancing precision and dexterity. The robotic arms mimic the movement of the human wrist, allowing for greater flexibility and control, especially in deep or narrow are difficult to access with standard instruments.
This technique provides:
- *3D high-definition imaging* with at least 10x magnification
- **The option to use *fluorescence cholangiography**, a special due to clearly visualize the bile ducts during surgery
These features help increase surgical safety and reduce the risk of converting to open surgery in complex cases.
2. Open cholecystectomy (OC)
- Doctor will make oblique incision below your right ribs cage.
- Doctor may prefer this procedure in some patients which expect to be difficult to remove the gallbladder with laparoscopic technique such as patient with multiple episode of gallstones attack, patient with history of abdominal surgery, patient with severe inflammation of gallbladder.
Consideration for Minimally Invasive Surgery or Open cholecystectomy depends on patients condition, patient preference and doctor expertise. In our hospital, most of our cholecystectomy successfully perform with Minimally Invasive technique.
Risk of Procedure
Specific risk
- CBD injury 0.3 – 1%
- Bleeding 1 – 2%
- Conversion to open surgery 2 – 10%
- Injury to other organs 0.3 – 1%
- Intra-abdominal abscess 1 – 2 %
- Incisional hernia 2 – 10%
General risk
- Pain
- Wound infection
- Lung collapse (Atelectasis)
- Clot in leg vein (Deep vein thrombosis)
Post-Operative
Common symptoms after surgery
Wound pain
- Although the incision is small, patient still experience wound pain.
- Severity of wound pain varies from person to person.
- Normally, doctor will prescribe pain medication for wound pain.
- If you still feel a lot of pain after medication, you can always call our staff.
Right shoulder pain
- It commonly occurs after laparoscopic surgery because of the gas from laparoscopic.
- This condition is transient and normally improves within 24-48 hours after surgery.
Bloating
- Some patients still feel a lot of gas in their stomach after surgery.
- This condition is transient and will improves over a period of time.
- It may takes 1-3 months after surgery until this symptoms is fully gone.
Recovery after surgery (In hospital)
Diet
- Normally, doctor will allow oral diet when patient is fully awake form anesthesia.
- In some special circumstances, such as difficult surgery, doctor may asks patient not to eat anything for another 1-2 days after surgery.
- It is preferable to avoid fatty meal for couple months.
- Our dietitian will help you with your diet as a part of our ERAS program.
Activities
- We encourage patient to have normal activities and move their body as soon as possible.
- The faster patient has activities, such as walking around their bed, the better for patient’s recovery.
- Our physical therapist will help you with your activities as a part of our ERAS program.
Intravenous fluid
- Normally, doctor will remove the intravenous fluid as soon as possible.
- The catheter may still attach for some of your medication and will be removed before your discharge
Medication
- You can take your personal medication after surgery which will be arranged by our staff.
- Doctor will prescribe pain killer or other medications to suit your condition.
Pain control
- Doctor will prescribe pain killer medication which mostly are in oral form.
- There’s also extra dose of pain medication to suit your need.
- Normally, the pain should not so intense. If you feel abnormally severe pain, please inform our staff immediately.
Post-discharge
Follow up
Follow up appointment
- Doctor will make an appointment about 1 week after the surgery.
- Doctor will examine your wound upon appointment.
- Doctor will also inform the pathology result of your resected gallbladder.
Follow up call
- There may be a call from our staff as a part of our services.
- Our staff will check for your symptoms and recovery.
- They will also remind you for your next appointment.
Report your symptoms
- If you feel anything wrong, please feel free to contact our staff and report your symptoms.
Long term follow up
- Normally, this procedure do not need long term follow up.