Hair Loss
- Seeing a large amount of hair in the drain after washing your hair
- Finding clumps of hair on the brush, pillow
- Noticing thinning hair or bald patches, reduced hair density at the crown, or a receding hairline
These signs indicate excessive hair loss and it’s advisable to consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
When is hair loss considered abnormal?
- Losing more than 70-100 hairs per day for those who wash their hair almost daily, or more than 200 hairs per day for those who wash their hair every 3-4 days.
- Hair loss during washing or drying in small amounts is normal. However, losing over 70-100 hairs per day during daily activities (e.g., on the pillow after waking, during meals, cooking, working) is considered abnormal.
- Patchy hair loss, where hair falls out and forms small coin-sized patches.

Causes
- Genetic Predisposition: The most common cause is a family history of baldness. Studies suggest that genetic and environmental factors like stress and pollution can trigger hair thinning, which is linked to the male hormone androgen.
- Stress, Illness, or Surgery: Long-term fever, childbirth, psychological stress, rapid weight loss, etc.
- Side Effects of Medications: For cancer, hypertension, arthritis, depression.
- Drug Allergies
- Radiation Therapy
- Infections: Fungal infections, syphilis, HIV, herpes.
- Skin Diseases: DLE and autoimmune diseases like SLE.
- Hormonal Issues: Thyroid problems, high or low hormone levels.
- Scalp Infections and diseases causing scarring, like lichen planus and certain types of lupus, can cause permanent hair loss.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, childbirth, stopping birth control pills, menopause.
- Stressful Events: Surgery, illness, or psychological trauma can cause temporary hair loss, which usually regrows without treatment.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of protein, iron, and other nutrients.
- Hair Damage: Tight hairstyles, hair rollers, ponytails, and braiding close to the scalp.
- Psychological Disorders: Twisting, pulling, or breaking hair due to psychological issues.

Diagnosis
Doctors will conduct a physical exam, inquire about medication use, and medical history of the patient and their family. Additional diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: To identify other causes of hair loss.
- Pull Test: To see how much hair comes out when gently pulled.
- Scalp Biopsy: Examining a scalp tissue sample under a microscope to determine the cause of hair loss.
Treatment
- Medication: Initial treatment often involves topical or oral medications prescribed by a specialist due to possible side effects.
- Hormonal Adjustment: For hair loss due to hormonal deficiencies.
- PRP Injection: Injecting platelet-rich plasma to stimulate stem cells in the hair roots.
- Laser Therapy: To address hair deterioration and strengthen hair roots.
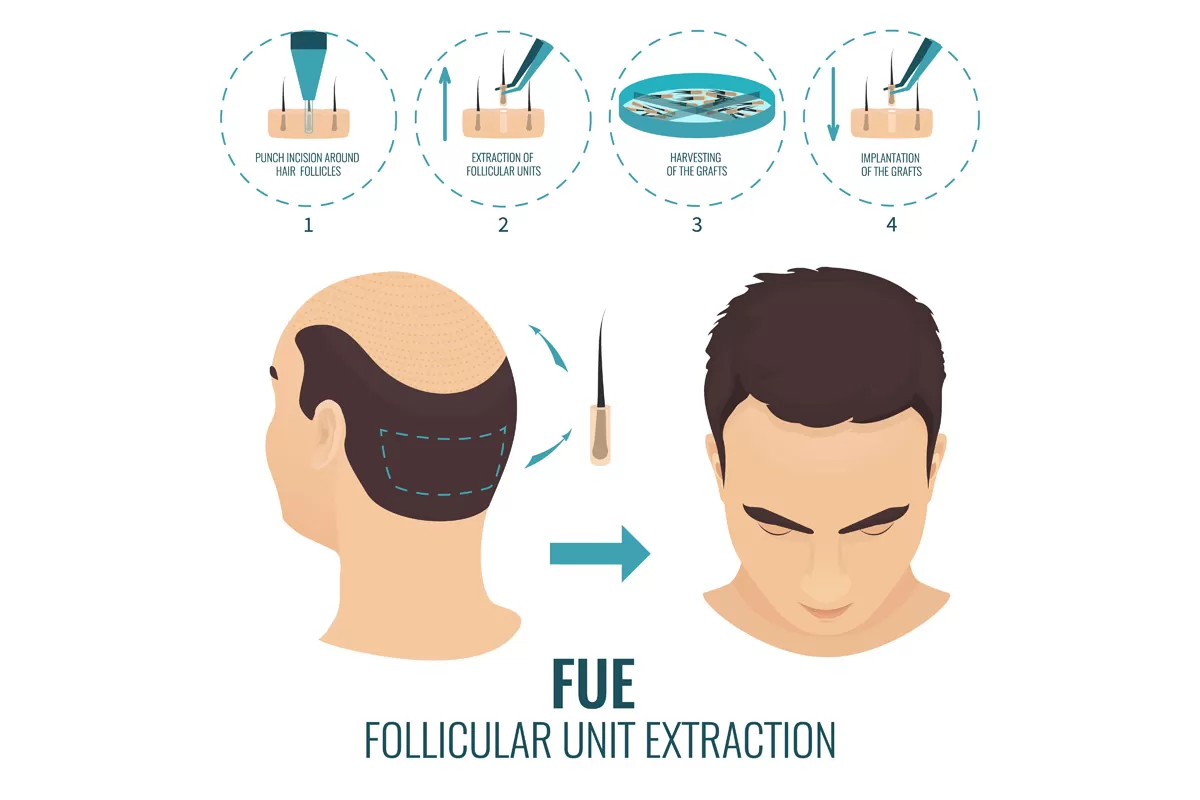
- Hair Transplant: Transplanting hair roots from unaffected areas to bald areas via surgery.
Prevention
Daily Self-Care:
- Balanced Diet: Include vitamins that nourish hair, like iron, zinc, vitamin D, B1, B3, B7 (biotin), and B12.
- Avoid Stress: Stress can increase hair loss; engage in stress-reducing activities like exercise, meditation, or sufficient rest.
- Avoid Hair Damage: Minimize the use of high heat on hair, such as blow dryers, straighteners, or frequent perming.
- Limit Hair Coloring: Avoid frequent chemical treatments, especially combined straightening, perming, and bleaching.
- Proper Hair Washing: Avoid very hot water and brushing wet hair.
- Maintain Scalp Hygiene: Regularly wash hair with suitable products that do not cause allergies, itching, dandruff, or scalp rashes.
- Scalp Massage: Gentle massage can improve blood circulation and promote hair growth.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Do not pull, twist, or rub hair excessively.
Specialized Products and Treatments:
- Shampoos and Conditioners: Use products designed to prevent hair loss or promote hair growth.
- Medications and Supplements: Supplements like biotin, minoxidil for hair loss issues.
- Laser Therapy: Low-Level Laser Therapy to stimulate hair growth.
- Hair Transplantation: For severe hair loss or baldness.
Daily hair and scalp care is crucial for preventing hair loss. If excessive hair loss occurs, consulting a doctor to determine the cause and appropriate treatment is advisable.