Stroke: A Medical Emergency — Early Detection Saves Lives
Cerebrovascular disease, commonly known as stroke, is a critical medical condition that requires urgent attention. Stroke can be classified into two main types:
- Ischemic Stroke This type occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the brain become narrowed or blocked, typically due to the buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) or calcium on the inner walls of the blood vessels. In some cases, ruptured plaques can cause clot formation, leading to sudden arterial obstruction.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke This occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding within or around the brain. The sudden loss of blood supply results in immediate brain tissue damage and often causes death if not treated promptly. Hemorrhagic strokes are more common in individuals with high blood pressure, cerebral aneurysms, liver disease, or blood disorders.
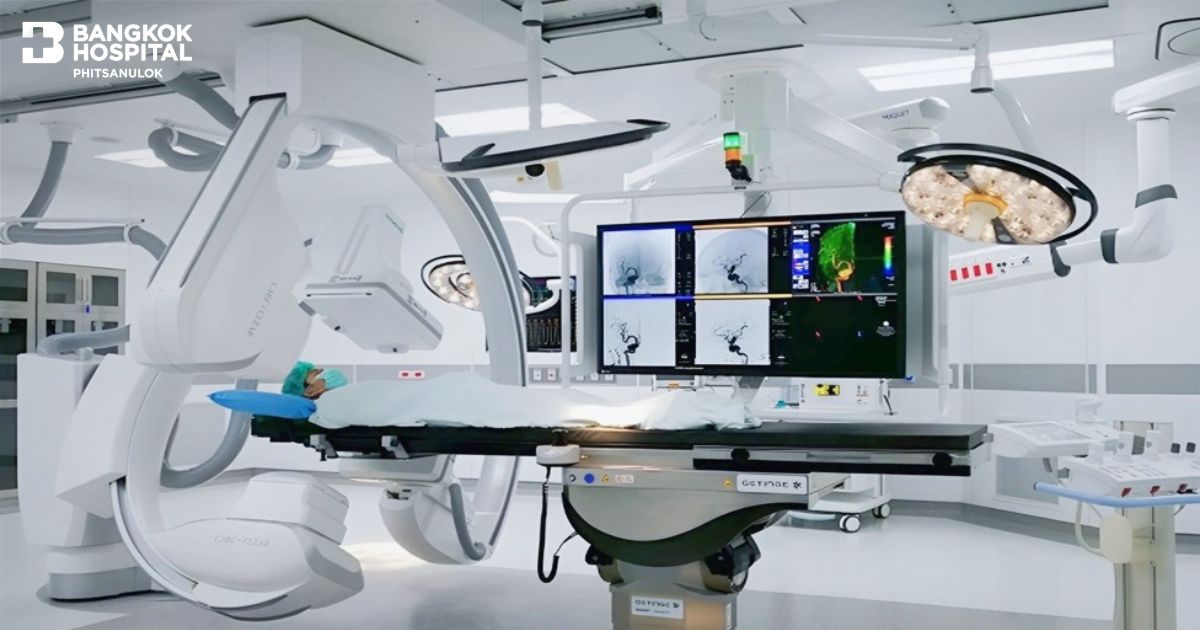
Early Diagnosis and Treatment with Bi-Plane DSA Technology
At Bangkok Hospital Phitsanulok, we utilize cutting-edge Bi-Plane Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) to diagnose and treat vascular diseases with exceptional precision.
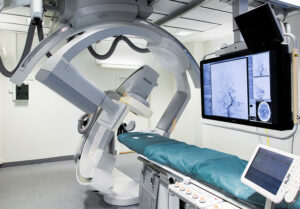
Key Advantages of Bi-Plane DSA:
-
Simultaneous dual-plane imaging (frontal and lateral views)
-
Ultra-high image resolution with clear visualization of even the smallest blood vessels
-
3D real-time imaging for accurate assessment of vascular abnormalities
-
Lower radiation exposure and contrast agent dosage, enhancing patient safety
-
Enables rapid, accurate diagnosis — crucial in emergencies such as stroke or heart attacks
-
Boosts diagnostic confidence and enhances treatment effectiveness
Biplane
is not only used for stroke and cardiovascular diseases, but also for conditions involving liver, limb, and systemic vascular systems. It offers a minimally invasive alternative to surgery, known as interventional radiology.
Act Fast When Stroke Symptoms Appear
Stroke symptoms appear suddenly and require immediate medical attention. Once a stroke is suspected, the patient must be brought to the hospital without delay. Timely diagnosis is essential to determine the type — ischemic or hemorrhagic — so that the appropriate treatment can be administered.
-
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Emergency surgery is often necessary to control bleeding.
-
Ischemic Stroke: The goal is to restore blood flow as quickly as possible. Ideally, a clot-busting drug (thrombolytic agent) should be administered within 4.5 hours of symptom onset. If that window is missed or the drug is ineffective, alternative treatments include:
1. Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis
For patients arriving between 3 to 6 hours after symptom onset or with large clots, medication is delivered directly to the blockage via a catheter inserted into the artery.
2. Mechanical Clot Retrieval
For patients arriving up to 8 hours after onset, a catheter is threaded from the groin artery to the site of blockage, where a special device captures and removes the clot.
3. Carotid Artery Stenting
If significant narrowing (over 50%) of the carotid artery is detected and surgery is not an option, a stent can be placed via a catheter from the groin or underarm. This procedure, which takes about 1–2 hours, is typically available in major private hospitals or teaching hospitals.
Preventing Stroke Recurrence
Stroke survivors are at increased risk of having another stroke. Preventive care is essential and includes:
-
Proper management of underlying conditions such as hypertension or diabetes
-
Adherence to prescribed medications
-
Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers
-
Sufficient rest and regular exercise
-
Avoidance of high-risk behaviors, such as:
-
High-fat or high-sodium diets
-
Smoking
-
Alcohol consumption
-