Overview
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a contagious illness caused by a group of enteroviruses, most commonly Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus 71 (EV71). This condition predominantly affects young children, especially those under the age of five, and can lead to severe complications in some cases.
Severe Complications
While many cases of HFMD are mild and self-limiting, infections caused by the EV71 strain can become life-threatening. Severe complications may include:
-
Neurological involvement such as seizures, drowsiness, vomiting, meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis, or acute flaccid weakness
-
Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle)
-
Acute pulmonary edema
-
In rare cases, survivors may suffer long-term neurological impairments
EV71 Vaccine
The EV71 vaccine provides protection against the EV71 virus — the primary cause of severe HFMD symptoms. It is recommended for children aged 6 months to 5 years, administered in two doses one month apart.
Please note that the EV71 vaccine only protects against the EV71 strain and does not prevent HFMD caused by other enteroviruses.
What is HFMD?
HFMD is a viral illness caused by enteroviruses, particularly Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus 71. It spreads easily among young children and poses a greater risk of severe illness in children under five years of age.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms typically appear as a group and may include:
-
Fever
-
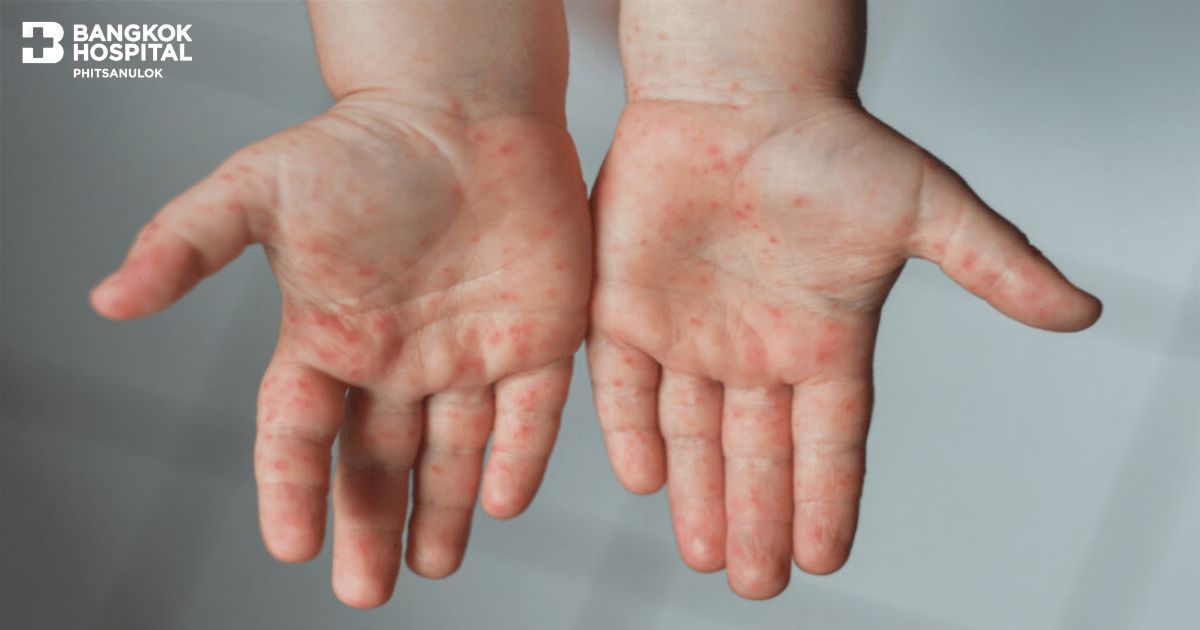
Red or fluid-filled blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth
-
Painful ulcers on the tongue, gums, and inner cheeks
-
Rash or blisters on the body, arms, or legs in some cases
Ulcers in the mouth are usually small and round, affecting the tongue, gums, inner cheeks, and the roof of the mouth. Although most children recover completely, some may experience serious neurological complications.
Severe Symptoms
Early-stage HFMD usually presents with mild fever and rashes that subside within 2–3 days. The rash typically resolves within 7–10 days. However, cases caused by the EV71 strain may lead to fatal complications, including:
-
Neurological conditions: seizures, lethargy, vomiting, meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis, and acute muscle weakness
-
Myocarditis and acute pulmonary edema
-
Possible long-term neurological damage in survivors
Outbreak Season
In Thailand, HFMD can occur year-round, but outbreaks are most common and severe from June to September (rainy season), and may persist through December. Increased vigilance and preventive measures are essential during these periods to reduce transmission risk.
Transmission
HFMD spreads through:
-
Saliva, nasal discharge, fluid from blisters, or feces of infected individuals
-
Contact with contaminated objects or surfaces
The virus can also be transmitted by asymptomatic individuals. Everyday activities like feeding, changing diapers, holding toys, or playing with infected children can result in the spread of the virus through hand contact with contaminated surfaces.
Reinfection and Viral Shedding
Even after recovery, children may continue to shed the virus in their stool for 6 to 8 weeks, posing a risk of further transmission. The virus can survive on surfaces for extended periods and is resistant to common disinfectants and alcohol-based sanitizers.
Treatment and Prevention
Currently, HFMD treatment is symptomatic. Management includes:
-
Isolating infected children to prevent further spread
-
Keeping children at home until full recovery
-
Temporarily closing schools or childcare centers during outbreaks for thorough cleaning
Preventive measures include:
-
Avoiding crowded areas, playgrounds, and shopping malls during outbreaks
-
Practicing good hygiene at home and in public spaces
-
Frequent handwashing and disinfecting toys and surfaces
For More Information
-
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/
-
LINE: https://lin.ee/h3jcNOO