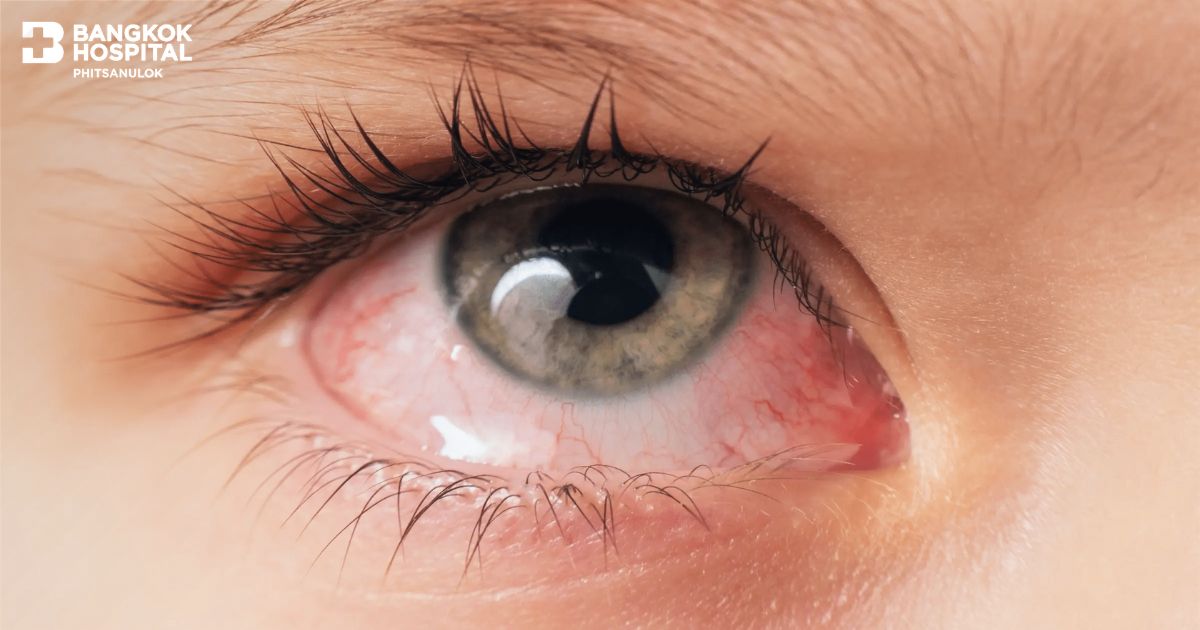
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Prevention and Treatment
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is one of the most prevalent eye conditions and can spread easily, particularly during seasonal weather changes or in crowded environments such as schools, offices, or military camps. It can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or allergens. While conjunctivitis is generally not severe, improper care can affect eye health and impair vision.
Causes of Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis may be triggered by several primary factors:
-
Viral Infection
-
The most common cause is a viral infection, typically from the adenovirus group. It spreads easily through direct contact with secretions such as tears, nasal mucus, or by sharing personal items.
-
Symptoms often include red eyes accompanied by cold-like symptoms such as fever, nasal congestion, and sore throat.
-
-
Bacterial Infection
-
Caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, or Haemophilus influenzae.
-
Characterized by thick yellow or green discharge that often crusts around the eyelashes, especially upon waking.
-
-
Allergic Conjunctivitis
-
Triggered by allergens such as dust, pollen, smoke, or chemicals.
-
Typically presents with red, itchy, and watery eyes, often accompanied by sneezing or nasal congestion.
-
-
Irritation from Foreign Substances
-
Exposure to smoke, dust, airborne particles, or chemicals (e.g., chlorine in swimming pools) can cause inflammation of the conjunctiva.
-
Common Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
-
Redness in one or both eyes
-
Excessive tearing
-
Itchy or irritated eyes
-
Eye discharge or crusting
-
Swollen eyelids
-
Sensitivity to light
Preventing Conjunctivitis
-
Frequent Hand Washing
-
Wash hands regularly with soap or alcohol-based hand sanitizers, especially after touching your face or eyes.
-
-
Avoid Rubbing the Eyes
-
Pathogens can be transferred to the eyes via contaminated hands.
-
-
Do Not Share Personal Items
-
Avoid sharing items such as handkerchiefs, towels, or cosmetics.
-
-
Clean Personal Belongings Regularly
-
Frequently wash pillowcases, bed linens, and towels.
-
-
Avoid Close Contact with Infected Individuals
-
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis can spread through direct contact.
-
-
Minimize Exposure to Allergens and Irritants
-
Those with allergies should avoid known triggers and follow medical advice regarding antihistamines or other medications.
-
Treatment of Conjunctivitis
-
Treat Based on the Underlying Cause
-
Viral Conjunctivitis: No specific treatment is required; symptoms usually resolve within 1–2 weeks. Rest and good hygiene are essential.
-
Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Requires antibiotic eye drops or ointments as prescribed by a physician.
-
Allergic Conjunctivitis: Treated with antihistamine or corticosteroid eye drops to reduce inflammation.
-
-
Relieve Irritation
-
Apply a clean, warm compress to the eyes to reduce swelling and discharge.
-
Avoid using contact lenses until symptoms are fully resolved.
-
-
Protect the Eyes from Bright Light
-
Wear sunglasses when outdoors if experiencing light sensitivity.
-
-
Maintain General Health and Nutrition
-
Eat foods rich in vitamins A and C to support overall eye health.
-