Currently, technological advancements have provided modern medicine with new tools for diagnosing and treating diseases, significantly improving patient treatment outcomes, and reducing death rates and disabilities.
Appropriate diagnostic and treatment
For the top three health conditions that cause the highest mortality rate among the population, namely cancer, accidents, and heart and vascular diseases, cancer has been the leading cause for many years. Before treating cancer, diagnosis is very important. Correct and clear diagnosis is necessary, starting with determining the disease stage (Staging), as an incorrect staging can lead to inappropriate treatment. During treatment, it is essential to have examinations that can serve as a good measure of treatment outcomes, as the disease and treatments can vary greatly among patients. A good measure can assess and predict treatment outcomes well, helping doctors choose the appropriate treatment and ensuring patients about their treatment outcomes. Currently, cancer is considered a chronic disease, meaning many patients can lead normal lives after treatment.
However, cancer can recur. Therefore, it’s crucial to evaluate and check for disease recurrence after treatment. Early detection of recurrent tumors (Recurrent Tumor) can lead to high treatment success.
PET-CT Scan for cancer detection
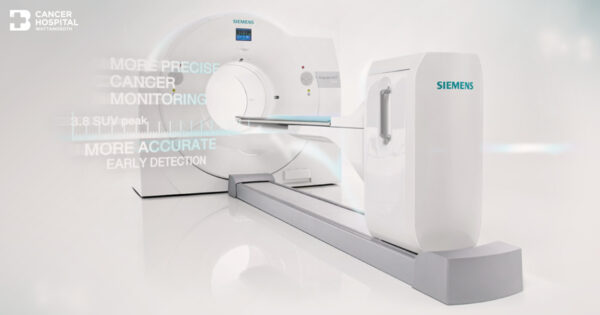
Radiology technology used in cancer patient examinations includes PET-CT machines, which can accurately determine disease stages, serve as treatment measures, and effectively detect cancer recurrence. Doctors can use PET-CT Scan in cancer patients comprehensively, applicable for almost all types of solid tumors, except for some cancers like prostate cancer.
PET-CT combines two types of radiological examinations in a single scan, allowing simultaneous patient examination and producing three sets of images: PET Scan images, CT Scan images, and a combination of both, the PET-CT Scan. The PET Scan process starts with injecting radiopharmaceuticals into the patient. Many types of radiopharmaceuticals are used for different types of cancer, but over 90% of cancers use the radiotracer FDG, a glucose derivative that emits positron radiation. FDG spreads throughout nearly all tissues in the body and concentrates heavily in solid tumor cancers. PET Scan imaging shows the distribution of radiation throughout the patient’s body, typically covering from the base of the skull to the bottom of the pelvis, areas where cancer often spreads. PET Scan is a highly sensitive biochemical examination, but its images alone cannot precisely locate the disease within the body. Simultaneous CT Scan imaging, combined with PET images, highlights the advantages of both scans: high sensitivity for disease detection and accurate disease localization through CT Scan images.
Studies have found that about 35% (about 1 in 3) of treatment plans are changed after PET-CT Scan examinations, thanks to the clearer and more accurate information provided. This makes PET/CT an essential tool for diagnosing cancer, determining disease stages, managing treatment, and checking for recurrence.
Besides cancer, doctors also use PET Scan effectively in treating several neurological diseases, such as various types of dementia (particularly Alzheimer’s disease) and identifying the origins of epilepsy using substances like FDG.
Moreover, many other radiopharmaceuticals can be used to diagnose other diseases, such as FDOPA for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis and C11-PIB, a radiotracer specifically for Alzheimer’s disease.
Source:
http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp
http://www.snmmi.org/NewsPublications/NewsDetail.aspx?ItemNumber=13252