Facts
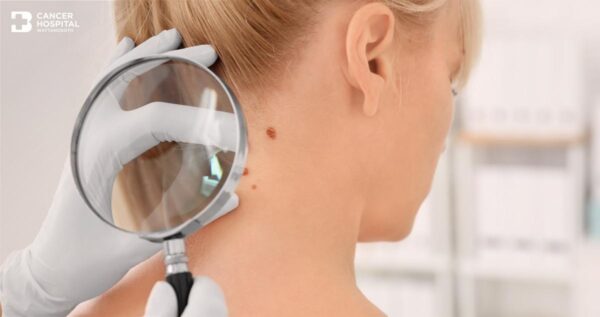
Skin cancer is cancer that develops on the skin due to abnormal growth of skin cells. There are several types of skin cancer which may include:
- Basal cell carcinoma Less severe skin cancer, occurs near the surface
- Squamous cell carcinoma Contains traits similar to basal cell carcinoma, however it grows and spreads faster. Usually the cancer will spread into deeper layers of the skin, often causing lumps to form.
- Malignant MelanomaThis cancer is a neoplasm of melanocytes or a neoplasm of the cells that develop from melanocytes. It is uncommon, but can be severe as it has high risk of spreading into the blood stream.
Skin cancer may continue to grow in size and spread to other vital organs such as the lymphatic glands. It is common found in individuals aged over 40 and is more common in men than women.